Introduction and Background
Almost 2.4 billion people lack access to improved sanitation worldwide. In today’s rapidly evolving world, the need for efficient and sustainable water and sanitation infrastructure is paramount.
However, the complexity of these projects often leads to delays, cost overruns, and suboptimal outcomes. To address these challenges, innovative solutions are required. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) offer a powerful toolkit to revolutionize the way we approach project pricing and management.
Towards the Sustainable Development Goals, 2030.
South Africa, along with other developing countries such as Tanzania, has struggled to make significant progress towards achieving the water and sanitation-related Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).

The importance of addressing this issue cannot be overstated. Developing countries lag in providing basic water and sanitation services has direct negative consequences on human development prospects, impacting all levels of society from individual to governmental.
Addressing this unmet need is essential for improving quality of life and supporting sustainable development.

Problem Statement
Why address water and sanitation project pricing?
Knowledge on the financial cost would help ensure sustainable management project finance. Financial resources for sanitation projects tend to be low in developing countries.
What challenges exist in pricing water and sanitation infrastructure?
- Limitations of traditional project pricing: Traditional project pricing methods often rely on manual calculations and subjective estimates. This can result in inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and a lack of transparency.
- Project implementation delays. Time lag between the inception and implementation stages of the water and sanitation infrastructure projects. This can cause variation in various parameters like cost of materials involved during project design and implementation phases.
- Unforeseeable challenges. The project implementation phase can experience various unexpected changes or variations that were not taken into account.
- Stakeholders’ involvement: Governments have the responsibility and
opportunity to stretch every dollar to ensure that more people have access to quality and reliable water and sanitation services, but this does not always happen. Project pricing can be influenced by political figures and private contractors who are after personal gains, potentially resulting in inflated costs due to lack of competition or the need for “unofficial” payments.” - Community participation: Some members do not fully participate in the early project inception phase meetings, which increases the risk of opposition once the project is implemented or details are revealed. This opposition leads to protests, legal challenges, and public hearings, all of which delay the project and increase costs due to extended timelines and potential redesigns.
How might we leverage Artificial intelligence and Machine Learning to ensure efficient pricing of water and sanitation public infrastructure?
Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning Solution

Traditional project pricing methods often rely on manual calculations and subjective estimates. This can result in inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and a lack of transparency. AI and ML can help overcome these limitations by providing data-driven insights and automating key processes.
There is an urgent need to use available digital tools and techniques (AI & ML) to improve public infrastructure investment efficiency. Leveraging existing public infrastructure project procurement datasets offers an opportunity to utilize artificial intelligence and machine learning to mitigate these inefficiencies, thereby improving
the efficiency of public water and sanitation infrastructure investments.
“AI Powered Infrastructure Precision“
Smart Infratrack Key Services
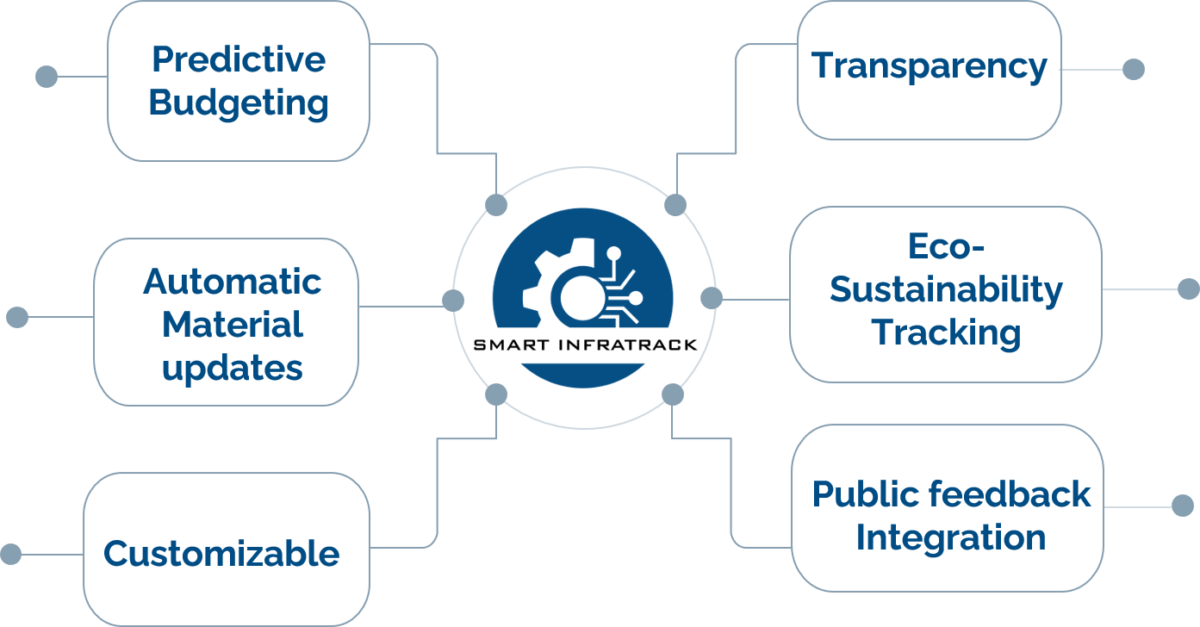
Predictive Budgeting
Using AI and ML, the system will offer accurate budget predictions based on real-time and historical data, helping stakeholders make informed decisions and mitigate risks related to cost overruns and project delays.
- Real-time monitoring: AI can continuously track project progress, identify potential bottlenecks, and suggest adjustments to the schedule.
- Predictive analytics: By analyzing historical data, AI can forecast potential delays or disruptions, allowing for proactive planning.
- Scenario modeling: AI can simulate various scenarios to assess the impact of different factors on project timelines and costs.
Automatic Material Schedule Updates
The material cost schedule will be automatically updated to adjust material costs based on real-time data to ensure that the project budget always reflects the most current material prices and usage information without the need for manual input
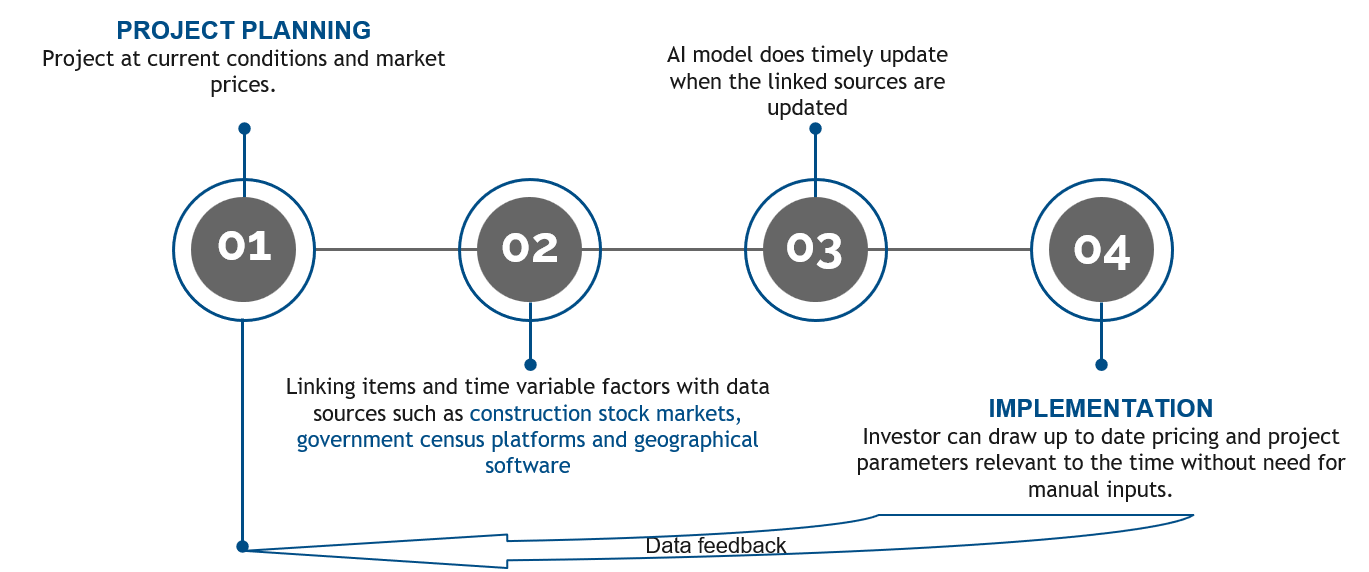
Transparency
Provide access to raw data related to the project, such as historical costs, ROI predictions, budget forecasts, and actual expenditures making it more transparent and accountable.
Customizable
To fit various country regulations and scopes
Public Feedback Integration
The system will actively involve the public in the decision-making process, collecting feedback and making it visible to ensure that projects meet community needs. Hence strengthening the legitimacy of public projects and builds trust.
Eco-Sustainability Tracking
As materials are selected, the system will automatically calculate the total carbon footprint based on the quantities and types of materials proposed, through integration of a carbon footprint database of construction materials.
System Architecture
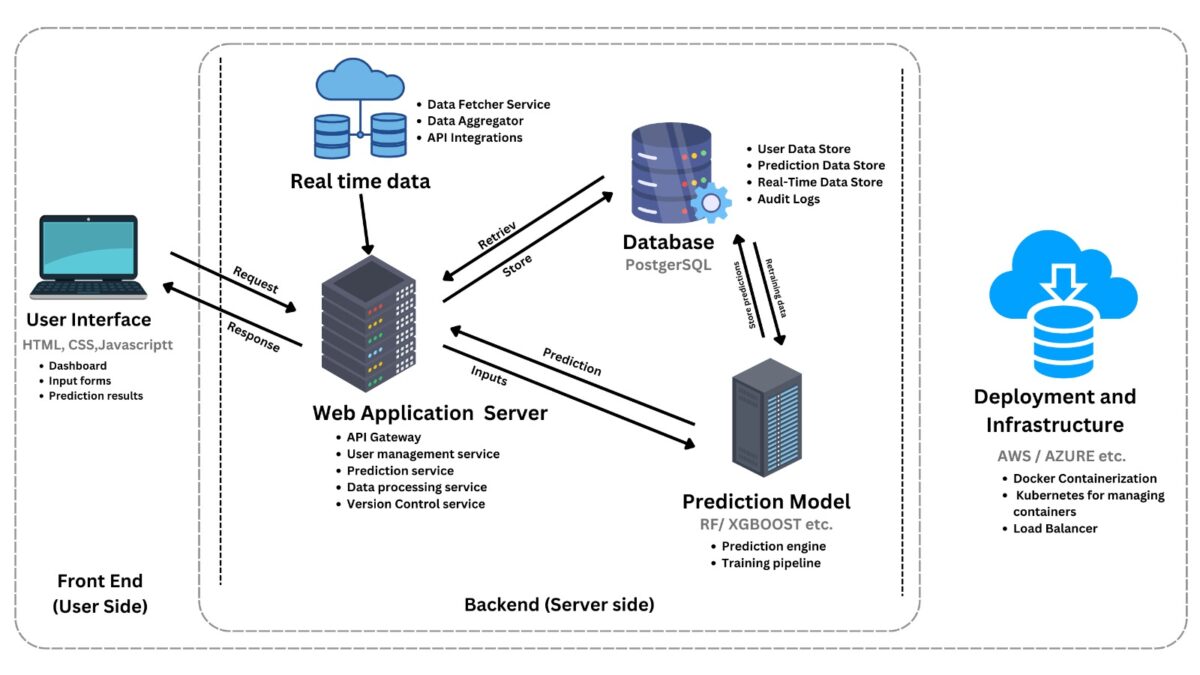
Key data sets required:

Machine Learning Flow Chart
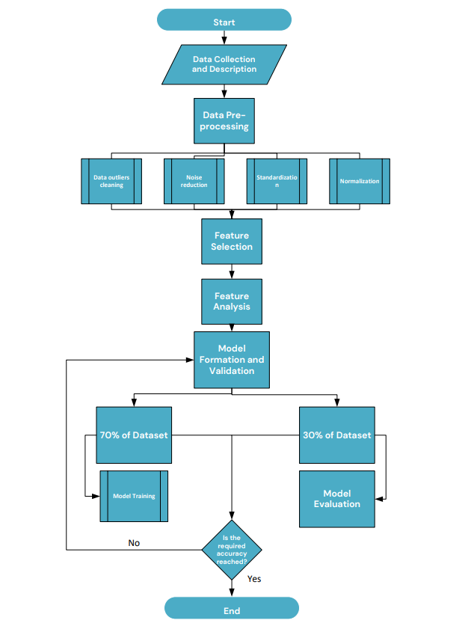
Machine Learning Algorithms
Random Forest
Is a powerful ensemble learning algorithm which gives an ideal choice for water and sanitation project budgeting tasks due to its robustness against overfitting and ability to handle a large number of input features.
It’s ability to provide feature importance scores gives an insight on which factors mostly influence the budget
Extreme Gradient Boosting
This excels in scalability across large datasets, it’s regularization capabilities prevent overfitting in case of noisy and high dimensional dataset
It’s ability to provide feature importance scores gives an insight on which factors mostly influence the budget
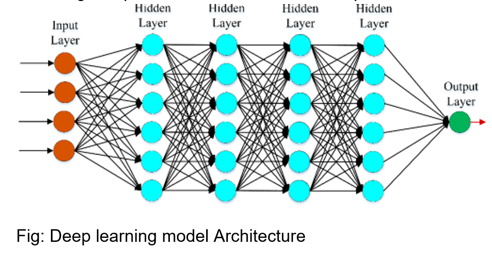
Deep Neural Networks (DNN)
Neural networks through processes like backpropagation and gradient descent optimization helps in learning complicated patterns in data. In this case it is suited for modelling complex and non-linear relationships in data.
Model Predictions
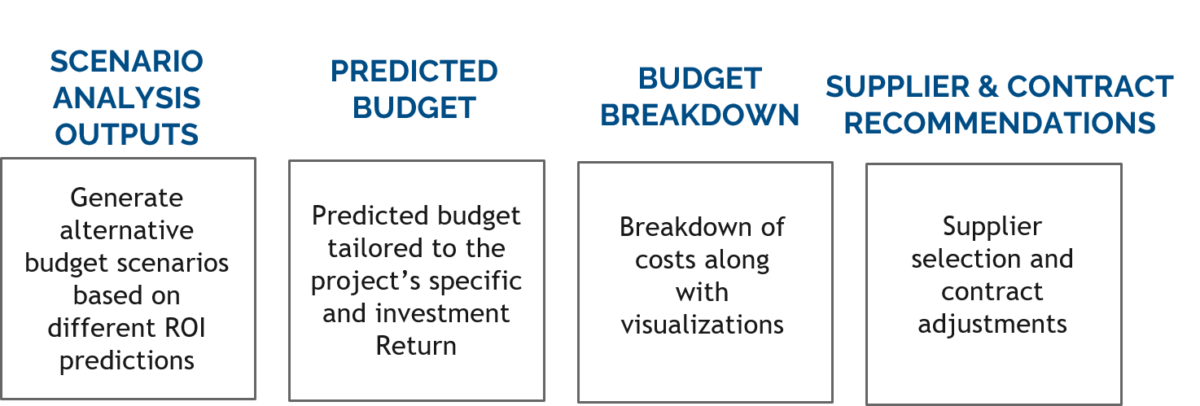
Cost Optimization:
- Material pricing analysis: AI can analyze market trends and identify cost-effective suppliers, helping to reduce material expenses.
- Resource allocation optimization: ML algorithms can optimize the allocation of resources (labor, equipment, materials) to minimize costs and maximize efficiency.
- Risk assessment and mitigation: AI can identify potential risks and suggest strategies to mitigate them, reducing the likelihood of unexpected cost increases.
Enhanced Decision-Making:
- Data-driven insights: AI can provide valuable insights into project performance, allowing stakeholders to make informed decisions.
- Predictive maintenance: AI can predict equipment failures, enabling preventative maintenance and reducing downtime costs.
- Demand forecasting: AI can forecast future water demand, helping to optimize infrastructure design and capacity.
User interphase
https://www.figma.com/design/jQG5b5jdzGf1LjSbzLDaKF/Smartifratrack?node-id=0-1&t=7HSTY6ZmN16NfSl9-1
System Security
Data Encryption
Encryption at Rest: Encrypt all stored data, including material costs, budget predictions, carbon footprint data, and public feedback. This will ensure that if the storage is compromised, the data remains inaccessible without the proper decryption keys.
Encryption in Transit: Encryption for all data transmitted between users, the system and external API’s
Access Control and Authentication
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Users may have access to budget
data while the public can view only non-sensitive information
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
Provision for MFA for all users, particularly those with administrative access, to add an extra layer of security beyond just a username and password.
Scalability Potential
Adaptable to Different Projects: Use of blockchain technology to ensure
the integrity and immutability of critical data such as budget records,
material cost updates, and public feedback. Blockchain can create a
tamper-proof ledger of all transactions and changes, ensuring that data cannot be altered without detection.
Global Reach: As a cloud-based service, the platform can be scaled and deployed globally, with local data integrations as needed.
Key Stakeholders and users
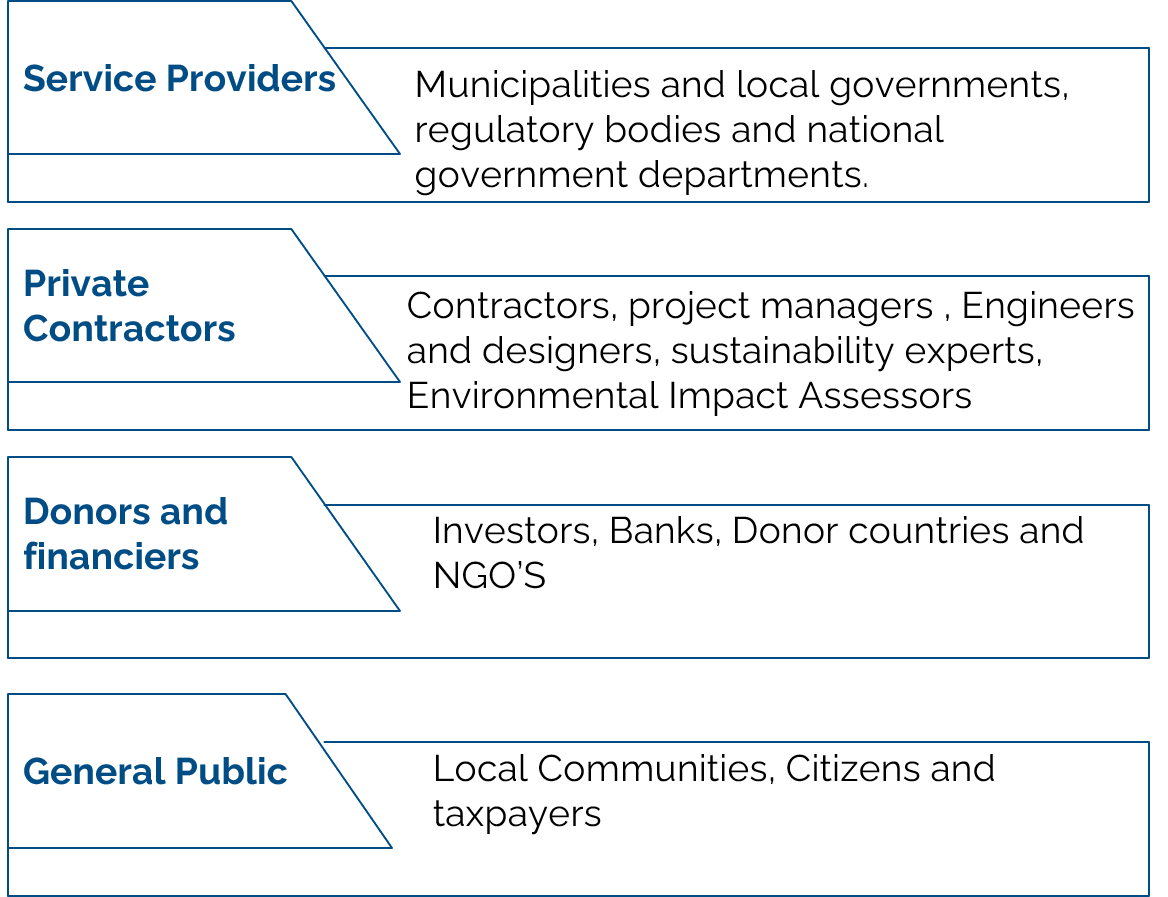
Benefits to stakeholders
- Consultants: Improved accuracy in project estimates, enhanced client satisfaction, and increased competitiveness.
- Government: More efficient allocation of resources, reduced project costs, and improved service delivery.
- Users: Reliable and affordable water and sanitation services, with minimal disruptions.
- Contractors: Optimized resource management, reduced risk, and improved profitability.
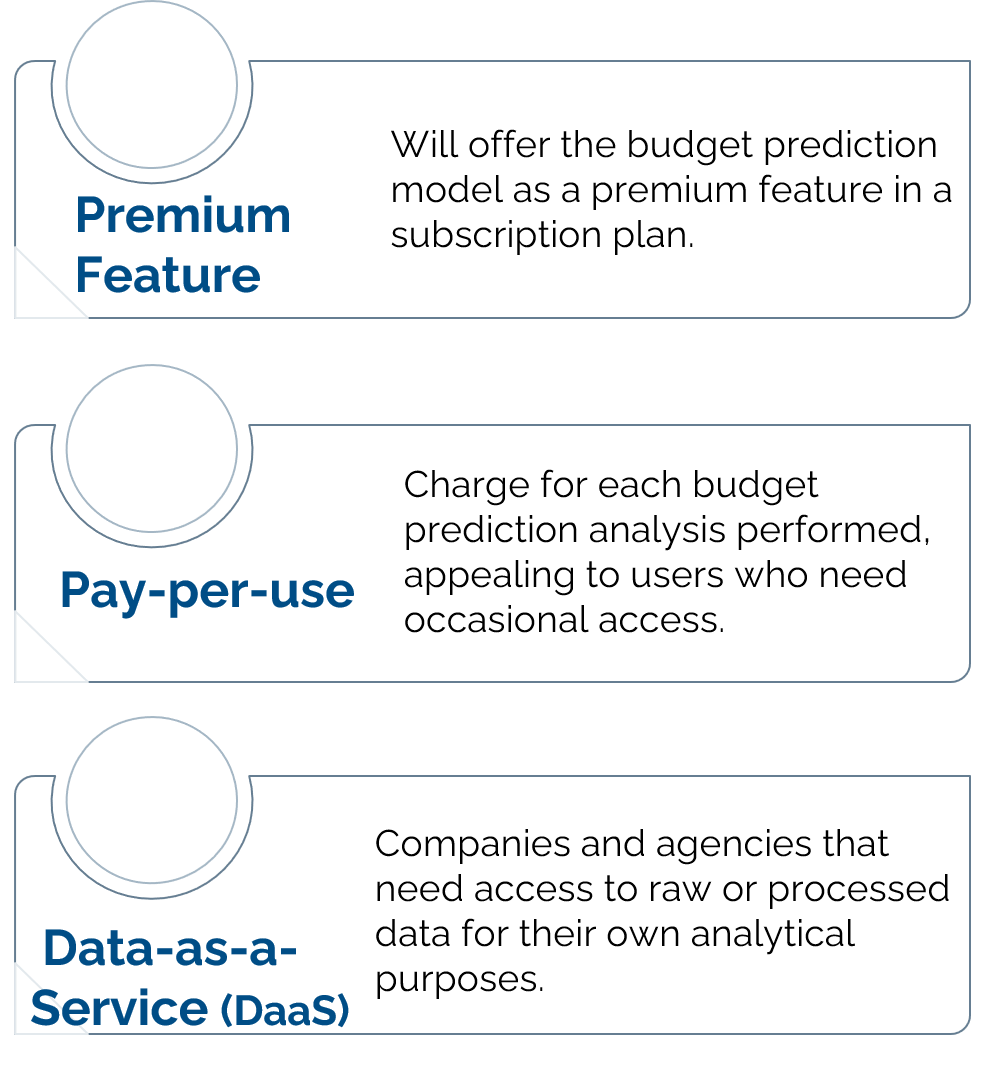
Proposed Business Model Integration
Team

